Many aspects of an electric vehicle are the same as a gas-powered one: the seats are seats, tires are tires, the steering wheel still turns right and left. The biggest difference, and the one that will make or break mass EV adoption, is the battery.
That’s why some of the most exciting research in the modern automotive landscape centers on battery technology—and “solid state” batteries are one area being explored. This alternative to the lithium-ion batteries used today promises to improve vehicle range, decrease charging times, and eliminate risk of battery fires.
You can’t yet drive a solid state battery-based EV off the lot, but they’re in the works. Toyota signed a manufacturing deal to commercialize its technology by 2028, which could eventually achieve over 900 miles of range. Honda is also working on them in its Tokyo-based lab, with plans to launch a vehicle with a solid-state battery in the latter part of the decade. Nearly all major EV brands are conducting similar research, such as Mercedes, Volkswagen, and China-based Nio.
In the future, trains, planes, and trucks may also use solid state batteries, setting the stage for much wider electrification of transportation than we can visualize today. Here’s what you need to know about this potentially game-changing technology.
What Is a Solid State Battery?

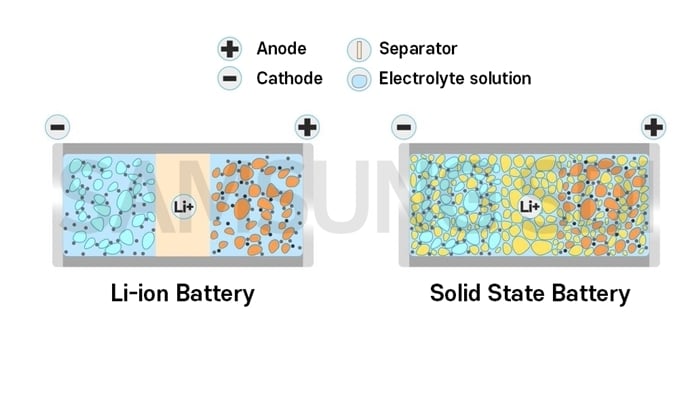
(Credit: Samsung)
Solid state batteries operate the same way as any other battery. They take energy in, store it, and release the power to devices—from Walkmen to watches and, now, vehicle motors. The difference is the materials inside.
Lithium-ion batteries, used in EVs today, have a liquid electrolyte solution sandwiched in between their cathodes and anodes (see the middle gap in the image above). Alternatively, solid state batteries use solid electrolytes.
The increased density means solid state batteries can hold anywhere between two to 10 times the capacity of a lithium-ion battery, AutoWeek reports.
Why Don’t EVs Already Use Solid State Batteries?
Solid state batteries already exist, just in much smaller devices like smartwatches, pacemakers, and RFID tags. The barrier to using them in EVs is primarily that they’re expensive and difficult to produce in a larger size at scale, Vox explains. With battery-powered vehicles already more expensive than gas-powered ones, consumers have little appetite for even pricier vehicles.
Certain aspects of the technology have yet to be figured out, such as longevity, but Honda says it has a solution. The solid electrolytes can degrade over time, so Honda plans to protect it by wrapping it in a new polymer fabric, Ars Technica reports. This is just one of many R&D efforts going toward this breakthrough chemistry from a slew of battery manufacturers and OEMs.
The batteries also need to undergo ample testing for durability on roads and lifespan for everyday driving. Remember, we’re talking about taking something worn on a wrist and using it to move a car or truck for the first time en masse. Best case scenario, we see luxury EVs with solid state batteries hitting the market in the 2030s.
Do Solid State Batteries Increase Range?

(Credit: xu wu / Getty Images)
With a solid state battery, EVs should be able to go just as far as a gas-powered car does before refueling. Take a 15-gallon gas tank that goes 30 miles per gallon, for example. That car can go 450 miles before filling up.
Most EVs today have ranges of 200 to 300 miles, although the Rivian R1T with a max pack battery goes 410 miles on a single charge, and the super-luxe Lucid, already on the road today, boasts a 516-mile range on the 2024 model.
Multiplying those ranges by around 50% (or as much as 80%, CarBuzz reports), and solid state batteries are ready to play ball on road trips. An EV with a 300-mile range now has 450 miles. Plus, solid state batteries will charge faster than lithium ion with less degradation to the battery itself.
Fires Extinguished: Solid State Improves EV Safety

(Credit: SpyroTheDragon / Getty Images)
With frightening reports of battery fires in the wake of flooding, EVs have developed a bad rep for being rolling matchsticks. But in reality, that honor should go to the lithium-ion battery. Swap it out for a solid state equivalent, and the EV has a very low risk of fire.
The liquid electrolytes in lithium-ion batteries are flammable, but since solid state batteries do not have that liquid, they do not run the same risk of fire.
Fires from lithium-ion batteries are rare, and automakers include casing and protective measures to avoid them, but when they happen they are powerful and difficult to extinguish, sometimes taking thousands of gallons of water. Building EVs that are not flammable is a big win for drivers, citizens, and fire departments.
How Do You Recycle Solid State Batteries?
Both lithium-ion and solid state batteries can be recycled in one of many new facilities dedicated to rejuvenating end-of-life material. For example, Redwood Materials, started by former Tesla co-founder J.B. Straubel, is a large scale battery recycling project in Nevada that includes Ford among its investors.
“Solid-state batteries are able to leverage the growing lithium-ion battery recycling infrastructure,” Will McKenna, head of marketing for BMW- and VW-backed Solid Power, tells CarBuzz.
Recommended by Our Editors
“Like [lithium-ion] batteries, Solid Power’s batteries typically contain nickel, manganese, lithium, and small amounts of cobalt. The same methods for recycling lithium-ion batteries by extracting these metals will also work for solid-state batteries. As such, we don’t anticipate additional processes of infrastructure investment required.”
Nightmare scenarios of piles of dead EV batteries leaking into the ground can also be dismissed, as there is no liquid inside to leak. Not to mention, solid state may have a 39% smaller carbon footprint than lithium-ion batteries, Electrek reports.
Solid State: Not the Only Breakthrough Battery
In a future where batteries power our electronics, cars, and even our homes and cities, we’ll need more than solid state batteries. Other breakthrough chemistries are in the works as well, such as silicon, graphene, and sodium batteries.
Porsche made a substantial investment in Group14, a Washington-based lab that’s currently providing automakers with its proprietary materials for silicon ion batteries.
“We’re increasing the battery’s energy density by up to 50% or more, and enabling battery manufacturers to bring charging times way down to the point where recharging your car gets closer to refilling your tank,” says Grant Ray of Group14.

Group14 website showing raw silicon battery materials (Credit: Group14)
The Biden administration has allocated billions in grant funding for battery companies, including Group14. Eonix, for example, is working on non-flammable batteries for the US military, and Lyten is making sulfur batteries for EVs. All have various benefits related to increased range, decreased charge times, longer lifespan, and improved safety.
Although battery development efforts are often portrayed as a “race” between technologies, they will likely coexist in a patchwork of solutions in the coming decades, with more advanced technology such as solid state reserved for deep-pocketed customers until the price (hopefully) comes down over time.
To learn more, see EV Batteries 101: Degradation, Lifespan, Warranties, and More.
Like What You’re Reading?
Sign up for Tips & Tricks newsletter for expert advice to get the most out of your technology.
This newsletter may contain advertising, deals, or affiliate links. Subscribing to a newsletter indicates your consent to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. You may unsubscribe from the newsletters at any time.






