

AI images generated on OpenAI’s DALL-E 3 will now have a watermark added to them from the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA).
C2PA is an open technical standard that allows publishers, companies, and others to embed metadata in media to verify its origin and related information.
The watermark is two-fold: there is a CR signature on the top left corner of each image and there is invisible metadata.
To check the provenance of an image, people can go to the Content Credentials Verify website and upload the image there. Only there will the CR tag appear.
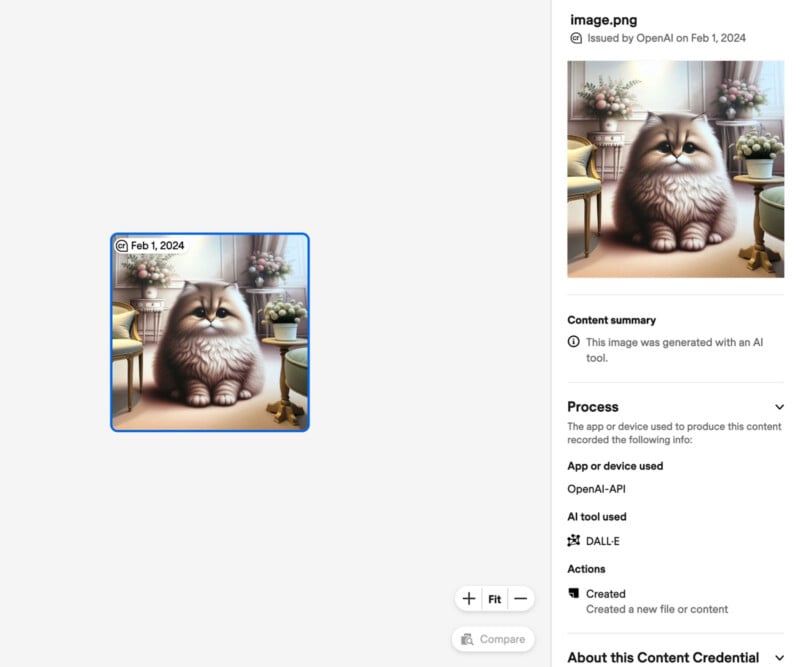
The watermark will appear on images generated from ChatGPT and via the API for the DALL-E 3 model and is working now — it will come into effect for mobile users on February 12.
“Metadata like C2PA is not a silver bullet to address issues of provenance,” OpenAI writes on its blog.
“It can easily be removed either accidentally or intentionally. For example, most social media platforms today remove metadata from uploaded images, and actions like taking a screenshot can also remove it. Therefore, an image lacking this metadata may or may not have been generated with ChatGPT or our API.
“We believe that adopting these methods for establishing provenance and encouraging users to recognize these signals are key to increasing the trustworthiness of digital information.”
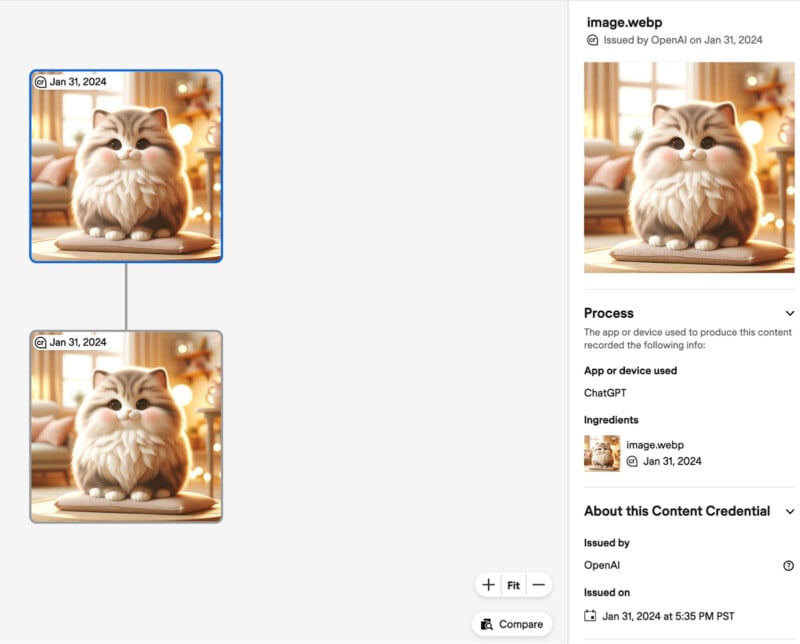
Last month, OpenAI said it was experimenting with its own provenance classifier; a new tool for detecting images generated by DALL-E. But there was no mention of that in the most recent update.
The C2PA digital signature system is not just for AI image generators, camera manufacturers such as Sony and Leica are incorporating it into their hardware. Adobe and Microsoft are also embracing it.
In fact, the Verify system was not designed to detect AI-generated images, it was made to recognize and confirm photos that include the CAI’s digital signature. However, the CR tag can be placed on AI images just like a real photo.






